Getting started
Requirements
- Python >= 3.10
Installation
pip3 install devsecops-engine-tools
Configuration
- Copy example_remote_config_local to the location where you want to store the remote configuration (either locally or in a git repository), and the folder name or repository name would be the one you should send in the --remote_config_repo flag.
For more information about structure remote config visit Structure Remote Config
Tools available for the modules
| Module | Tool | Type |
|---|---|---|
| ENGINE_RISK | DEFECTDOJO | Free |
| ENGINE_IAC | CHECKOV | Free |
| KUBESCAPE | Free | |
| KICS | Free | |
| ENGINE_DAST | NUCLEI | Free |
| ENGINE_SECRET | TRUFFLEHOG | Free |
| GITLEAKS | Free | |
| ENGINE_CONTAINER | PRISMA | Paid |
| TRIVY | Free | |
| ENGINE_DEPENDENCIES | XRAY | Paid |
| DEPENDENCY CHECK | Free | |
| TRIVY | Free | |
| ENGINE_FUNCTION | PRISMA | Paid |
| ENGINE_CODE | BEARER | Free |
| KIUWAN | Paid |
Scan running - (CLI) - Flags
devsecops-engine-tools --platform_devops ["local","azure","github"] --remote_config_source ["local","azure","github"] --remote_config_repo ["remote_config_repo"] --remote_config_branch ["remote_config_branch"] --module ["engine_iac", "engine_dast", "engine_secret", "engine_dependencies", "engine_container", "engine_risk", "engine_code", "engine_function"] --tool ["nuclei", "bearer", "checkov", "kics", "kubescape", "trufflehog", "gitleaks", "prisma", "trivy", "xray", "dependency_check"] --folder_path ["Folder path scan engine_iac, engine_code, engine_dependencies and engine_secret"] --platform ["k8s","cloudformation","docker", "openapi", "terraform"] --use_secrets_manager ["false", "true"] --use_vulnerability_management ["false", "true"] --send_metrics ["false", "true"] --token_cmdb ["token_cmdb"] --token_vulnerability_management ["token_vulnerability_management"] --token_engine_container ["token_engine_container"] --token_engine_dependencies ["token_engine_dependencies"] --token_external_checks ["token_external_checks"] --xray_mode ["scan", "audit","build-scan"] --image_to_scan ["image_to_scan"] --dast_file_path ["dast_file_path"] --context ["false", "true"] --terraform_repo_root ["terraform_files_repo"] --docker_address ["docker addres to engine_container with Prisma tool"]
Scan running sample (CLI) - Local
Complete the value in .envdetlocal file a set in execution environment
$ set -a
$ source .envdetlocal
$ set +a
devsecops-engine-tools --platform_devops local --remote_config_source local --remote_config_repo DevSecOps_Remote_Config --module engine_iac
Scan running sample - Azure Pipelines
Note: If the remote configuration is in an Azure Devops repository. the tool gets the token from the SYSTEM_ACCESSTOKEN variable to get the remote configuration repository. You must ensure that this token has permission to access this resource.
name: $(Build.SourceBranchName).$(date:yyyyMMdd)$(rev:.r)
trigger:
branches:
include:
- trunk
- feature/*
stages:
- stage: engine_tools
displayName: Example Engine Tools
jobs:
- job: engine_tools
pool:
name: Azure Pipelines
steps:
- script: |
# Install devsecops-engine-tools
pip3 install -q devsecops-engine-tools
devsecops-engine-tools --platform_devops azure --remote_config_source azure --remote_config_repo remote_config --module engine_iac
displayName: "Engine Tools"
env:
SYSTEM_ACCESSTOKEN: $(System.AccessToken)
Scan running sample - Github Actions
If remote config is in a GitHub repository, either public or private.
If the repository is public:
- The yml file containing the workflow should be configured using the default secret GITHUB_TOKEN. For more information, refer to Automatic token authentication.
If the repository is private:
-
Create a personal access token with the necessary permissions to access the repository.
-
Add the token as a secret in the GitHub repository.
-
Configure the yml file containing the workflow using the created secret.
Example of the workflow yml:
name: DevSecOps Engine Tools
on:
push:
branches:
- main
- feature/*
env:
GITHUB_ACCESS_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GH_ACCESSTOKEN }} #In this case, the remote config repository is private
# When the remote config repository is public, the secret should be like this: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
jobs:
release:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Set up Python
uses: actions/setup-python@v5
with:
python-version: "3.12"
- name: Set up Python
run: |
# Install devsecops-engine-tools
pip3 install -q devsecops-engine-tools
output=$(devsecops-engine-tools --platform_devops github --remote_config_source github --remote_config_repo remote_config --module engine_iac)
echo "$output"
if [[ $output == *"✘Failed"* ]]; then
exit 1
fi
Scan running sample (Docker)
Installation
docker pull bancolombia/devsecops-engine-tools
docker run --rm -v ./folder_to_analyze:/folder_to_analyze bancolombia/devsecops-engine-tools:latest devsecops-engine-tools --platform_devops local --remote_config_source local --remote_config_repo docker_default_remote_config --module engine_iac --folder_path /folder_to_analyze
The docker image have it own default remote config with basic configuration called docker_default_remote_config, but you can define your own config and pass it as volume
docker run --rm -v ./folder_to_analyze:/folder_to_analyze -v ./custom_remote_config:/custom_remote_config bancolombia/devsecops-engine-tools:latest devsecops-engine-tools --platform_devops local --remote_config_source local --remote_config_repo custom_remote_config --module engine_iac --folder_path /folder_to_analyze
Metrics
With the flag --send_metrics true and the configuration of the AWS-METRICS_MANAGER driven adapter in ConfigTool.json of the engine_core the tool will send the report to bucket s3. In the metrics folder you will find the base of the cloud formation template to deploy the infra and dashboard in grafana.
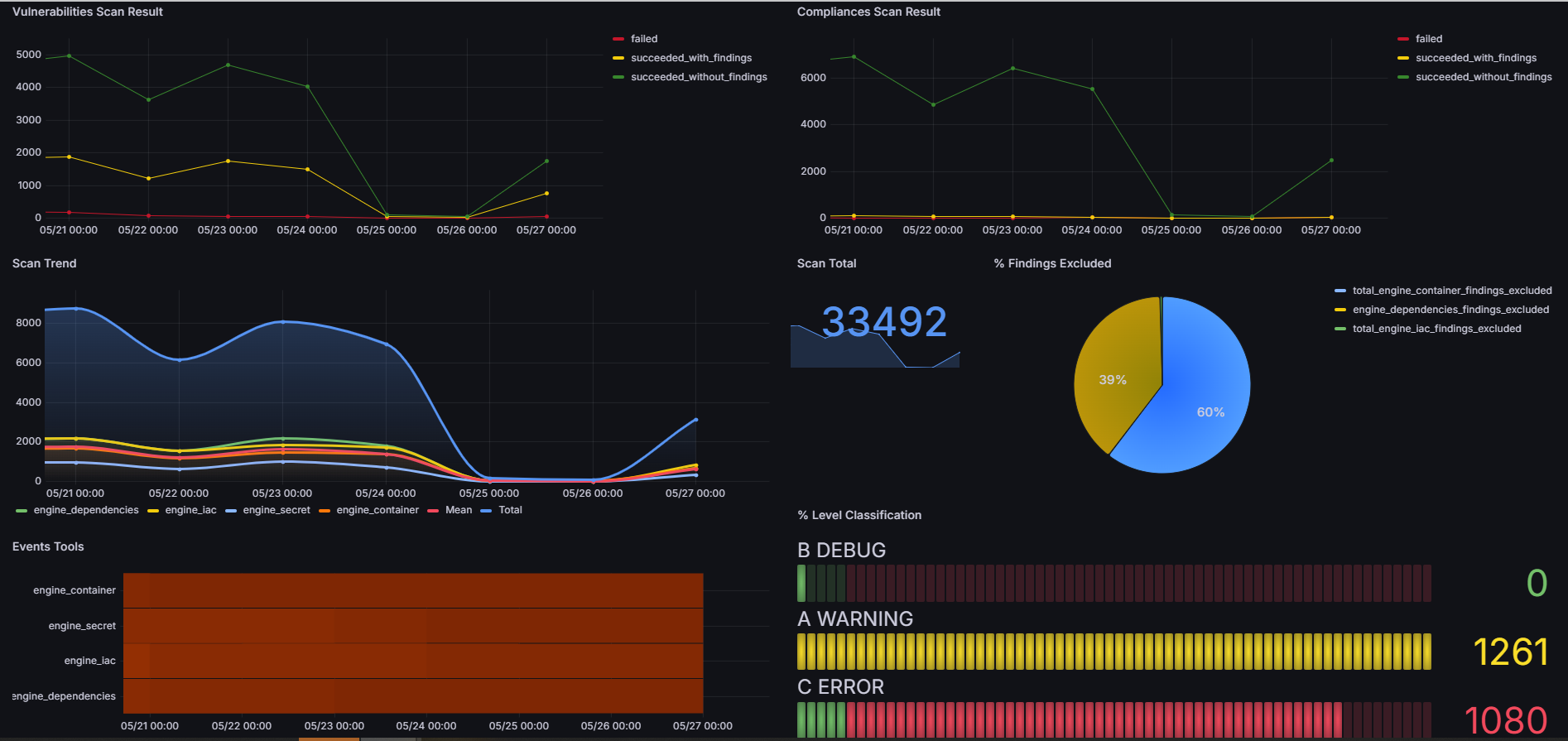
Config Tool Generator
To generate the ConfigTool.json file in a simple way, a web interface was created where you can configure each necessary parameter individually or use a base template that you want to modify. In the config tool generator folder you will find the code for the SPA created in Angular to run it local environment.

